Auditing
Auditing is a crucial aspect of security and compliance for extensions built into the Q2 Online Banking platform. Auditing allows the tracking of events that occur within the system, providing a way to monitor actions, protect key methods, and ensure accountability.
How are audit events used?
Audit events are used to log actions taken by users or the system within the Q2 Online Banking platform. These events can include user logins, transactions, changes to account settings, and other critical events. By capturing these events, we can maintain a record of activities, which is essential for compliance with regulatory requirements and for investigating potential security incidents. Audit events can be used in connection with Q2 Patrol to trigger additional security measures, such as step-up authentication via Event Driven Validation (EDV). They can be connected to CSR assist policies to provide additional control and protections around access for CSRs assisting end users. Audit events can also be used for reporting and analytics, helping institutions understand user behavior and improve their services. Adding events to important methods can provide additional hooks for Audit Action Extensions and EDV Adapters to build additional functionality around.
Implementing Audit Events
Audit events should be implemented on any of your server methods that perform critical actions or handle sensitive data. Any methods you create that modify user data, perform transactions, or access sensitive information should have audit events associated with them. To do this, you will first need to define the audit actions in your extension’s DB Plan. Once defined, you can use the provided Python decorator to easily add auditing to your server-side methods.
Creating New Audit Events
To create a new Audit Actions for your extension, you will define the action in your extension’s db_plan.py file. This is done by adding an entry to self.audit_actions. Each entry defines a new audit action with the action name, action description, and the category of action.
self.audit_actions = [
db_plan.AuditAction("CustomAuditAction", "Custom Audit action for extension name submit request", "SDK"),
...
]
Decorating Methods for Auditing
The @create_audit decorator simplifies the process of auditing events by allowing you to easily log important actions taken in your extensions. By applying this decorator to your server-side methods, you can ensure that audit events are created automatically whenever those methods are invoked.
from q2_sdk.core.http_handlers.tecton_server_handler import Q2TectonServerRequestHandler, create_audit
class AuthorizedUserHandler(Q2TectonServerRequestHandler):
@create_audit(audit_action_name="CustomAuditAction")
async def submit(self):
"""
This route will be only called after an audit event has been created
"""
When using an audit action name, the decorator creates audit details with basic information such as the extension name and routing key. You can also provide an audit details object to include additional context in the audit event. The audit details parameter accepts a string, dictionary, or a lambda that returns a dictionary. If you use a lambda, it will be executed when the audit event is created, allowing you to include dynamic information from your handler in the audit details.
from q2_sdk.core.http_handlers.tecton_client_handler import Q2TectonClientRequestHandler, create_audit
class AuthorizedUserHandler(Q2TectonClientRequestHandler):
@create_audit(
audit_action_name="CustomAuditAction",
audit_details="Example details"
)
async def string_details(self):
"""
"""
@create_audit(
audit_action_name="CustomAuditAction",
audit_details={"key": "value"}
)
async def dict_details(self):
"""
"""
@create_audit(
audit_action_name="CustomAuditAction",
audit_details=lambda self: {"detailItem": self.form_fields.detail_item, "firstName": self.online_user.first_name}
)
async def lambda_details(self):
"""
"""
You may also pass a error handler method to the decorator to handle cases where Q2 Patrol indicates Event Driven Validation (EDV) is required for your audit event and an exception is thrown during the process.
from q2_sdk.core.http_handlers.tecton_server_handler import Q2TectonServerRequestHandler, create_audit
class AuthorizedUserHandler(Q2TectonServerRequestHandler):
def handle_edv_error(self, error):
template = self.get_template(
"error.html.jinja2",
{
"header": "MyExtension: Error",
"message": f'EDV Failure - {error}',
},
)
html = self.get_tecton_form(
"MyExtension",
custom_template=template,
# Hide the submit button as there is no form on this route.
hide_submit_button=True,
)
return html
@create_audit(audit_action_name="CustomAuditAction", error_handler=handle_edv_error)
async def submit(self):
"""
This route will be only called after an audit event has been created
"""
Error Handling
Client-side and server-side error handling is important to ensure a smooth user experience when an audit event is denied or step-up authentication fails. As shown above, both client-side and server-side extensions allow a custom error handler to be provided to manage these scenarios. If you do not provide a custom error handler, the SDK will provide some default error handling mechanisms.
With server-side extension handling, the SDK and Online Banking platform can manage returning an appropriate error response to the client which will open an modal if the user is blocked or unable to complete the process.
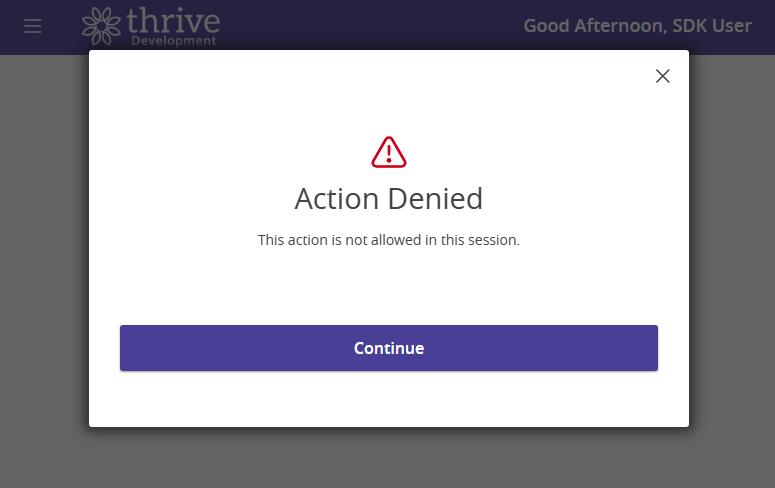
Client-side extensions should be prepared to handle error responses from the server on any routes they call that are decorated for auditing. This may include displaying an error message to the user or redirecting them to a different page.
tecton.sources.requestExtensionData({
route: 'my_audited_route',
body: { 'key': value }
}).then(response => {
// Handle successful response
}).catch(error => {
tecton.actions.showModal({
title: error.message,
message: error.data.detail,
modalType: 'error'
});
});